|
|
On the most important:
|
Science reporting session

|

Abstracts 2011

Abstracts 2012

Abstracts 2013

Abstracts 2014
|

He main directions of development of hydrogen energy (review)

Hydrogen energy: storage and transportation of hydrogen (review)
|

Monograph.
Basic problem of hydrogen energy.
|
|
|
|
|
Influence of the phase and structural states on hydrogen - sorption properties of hetero phase alloys of the Ti - Fe - Mn and Ti - Zr - Mn - V systems
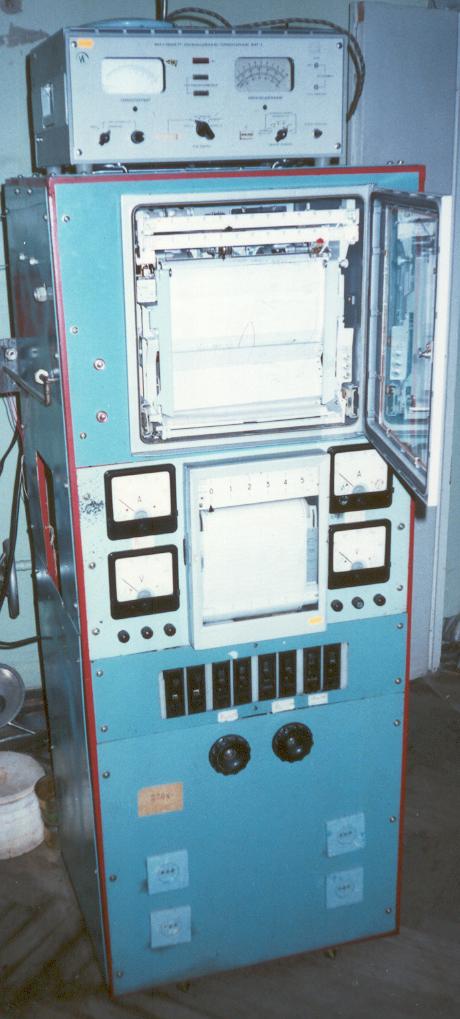
General view of the apparatus IVGM-2M to study the interaction of hydrogen with metals.Area of applications
It is expected to develop a series of new domestic alloys for hydrogen accumulation with the improved sorption properties and high hydrogen capacity. Alloys will be used for the hydrogen energy needs and for safe transportation and storage of hydrogen.
Brief description
Natural composites formed by eutectic crystallization, consisting of bcc β (Ti, Zr, Mn) solid solution and (Ti,Zr)Mn2-х Laves phase are suitable materials for hydrogen accumulation. β (Ti, Zr, Mn) solid solution has high hydrogen capacity while Laves phase is characterized with acceptable working temperature, easy surface activation, and has significant interface area free of oxide films. Combining of the advantages of both these phases leads to a substantially increased sorption capacity and improved kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of hydrogenation and dehydrogenation processes. The solid solution based on titanium absorbs hydrogen with kinetics similar to hydrogen sorption kinetic of intermetallics and in a short time achieves high hydrogen storage capacity.
Expected results
Optimization of the developed alloys will create a new class of materials - hydrogen accumulators with improved sorption properties and high hydrogen capacity for hydrogen energetic needs.
Advantages
Solid solution based on titanium in eutectic composition absorbs hydrogen with kinetics similar to hydrogen sorption kinetics of intermetallic and in a short time achieves high hydrogen storage capacity. This feature is associated with a high surface area of the interface, typical eutectic structures for which the hydrogen diffusion coefficient is approximately 103 times higher than the volume diffusion. Process of hydrogenation occurs avalanche-like due to brittleness of Laves-phase, which leads to rapid cleavage of formed hydride and the formation of clean surface ready for hydrogen sorption. Also hydrogen capacities of each of the phases in eutectic structure upon hydrogenation exceed their capacity at individual hydrogenation under the same conditions.
Competitors
Department of Chemistry and Physics of High Pressure of Chemical Faculty of M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University (Russia).
Project development
During the 2011-2014 hydrides have been synthesized; the structure and phase composition of the products of hydrogenation of Ti-Fe-Mn, Ti-Zr-Mn and Ti-Zr-Mn-V alloys have been investigated. The influence of the eutectic degree of alloys on sorption and reversible capacity and kinetic parameters of hydrogen sorption and desorption processes has been determined.
Intellectual property
-
Patent on useful model № 77457 Ukraine (11.02.2013) Alloys for hydrogen storage / Ivanchenko V.G., Pryadko T.V., Dekhtyarenko V.A.
- Patent on useful model № 82647 Ukraine (12.08.2013) Hydrogenated titanium based alloys for neutron protection / Pryadko T.V., Ivanchenko V.G., Dekhtyarenko V.A.
- Patent on useful model №82925 Ukraine (27.08.2013) Alloys for hydrogen storage / Ivanchenko V.G., Pryadko T.V., Dekhtyarenko V.A.
- Patent for an invention №103865 Ukraine (25.11.2013) Hydrogenated titanium based alloys for neutron protection / Pryadko T.V., Ivanchenko V.G., Dekhtyarenko V.A.
Contact information
Executor: G.V.Kurdyumov Institute of metal-physics of National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine
Project № 26 “Influence of the phase and structural states on hydrogen - sorption properties of hetero phase alloys of the Ti - Fe - Mn and Ti - Zr - Mn - V systems”
Contact person:

Ivanchenko Volodymir G.
Tel. +38(044)- 424-12-20
Е-mail: ivanch@ imp.kiev.ua
|